H5n1 who – H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has raised global concerns due to its potential threat to human health and the poultry industry. This comprehensive guide explores the nature, transmission, and implications of H5N1, shedding light on its impact on poultry, livestock, and human health.
From its origins and history to the latest research and development efforts, this guide provides a thorough overview of H5N1, empowering readers with the knowledge to understand and respond to this evolving virus.
Avian Influenza H5N1: H5n1 Who
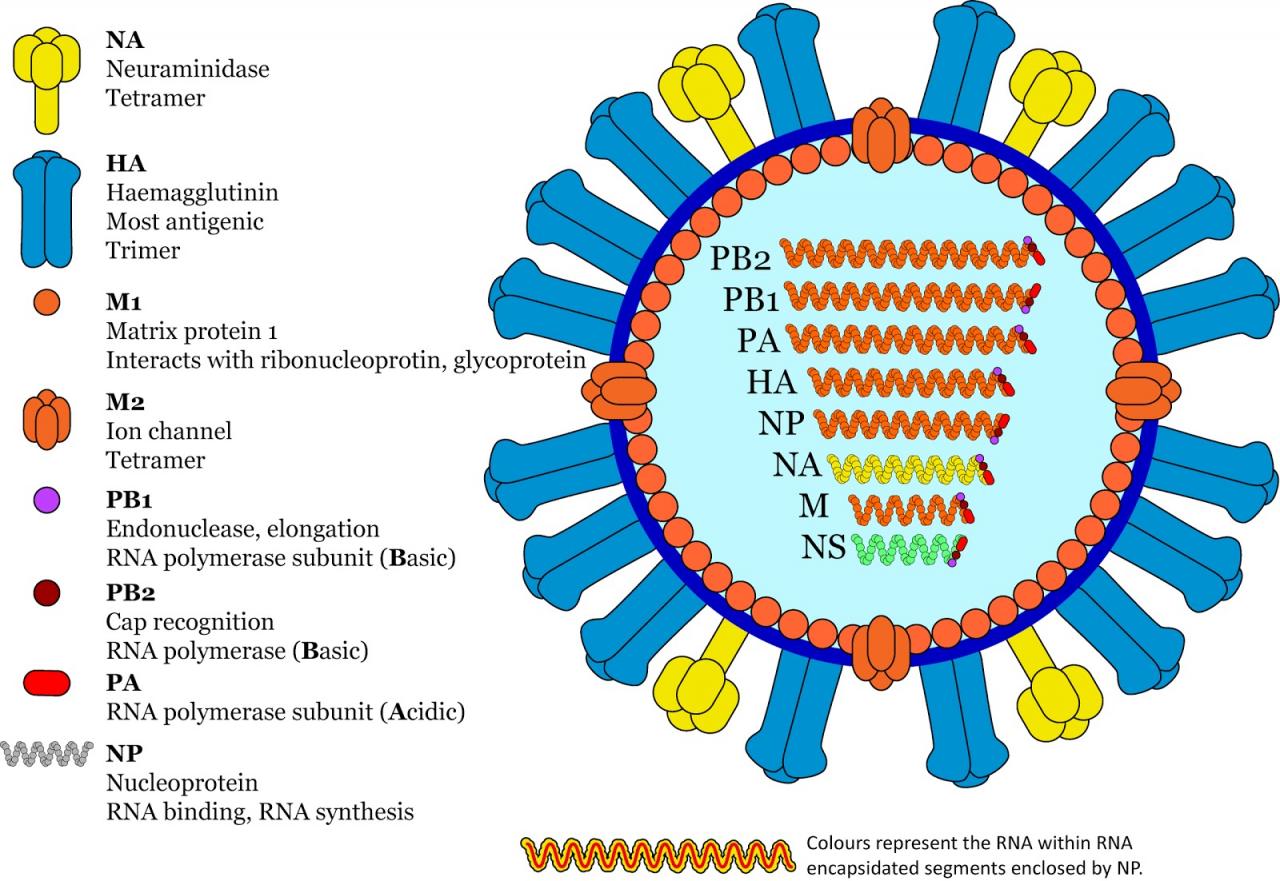
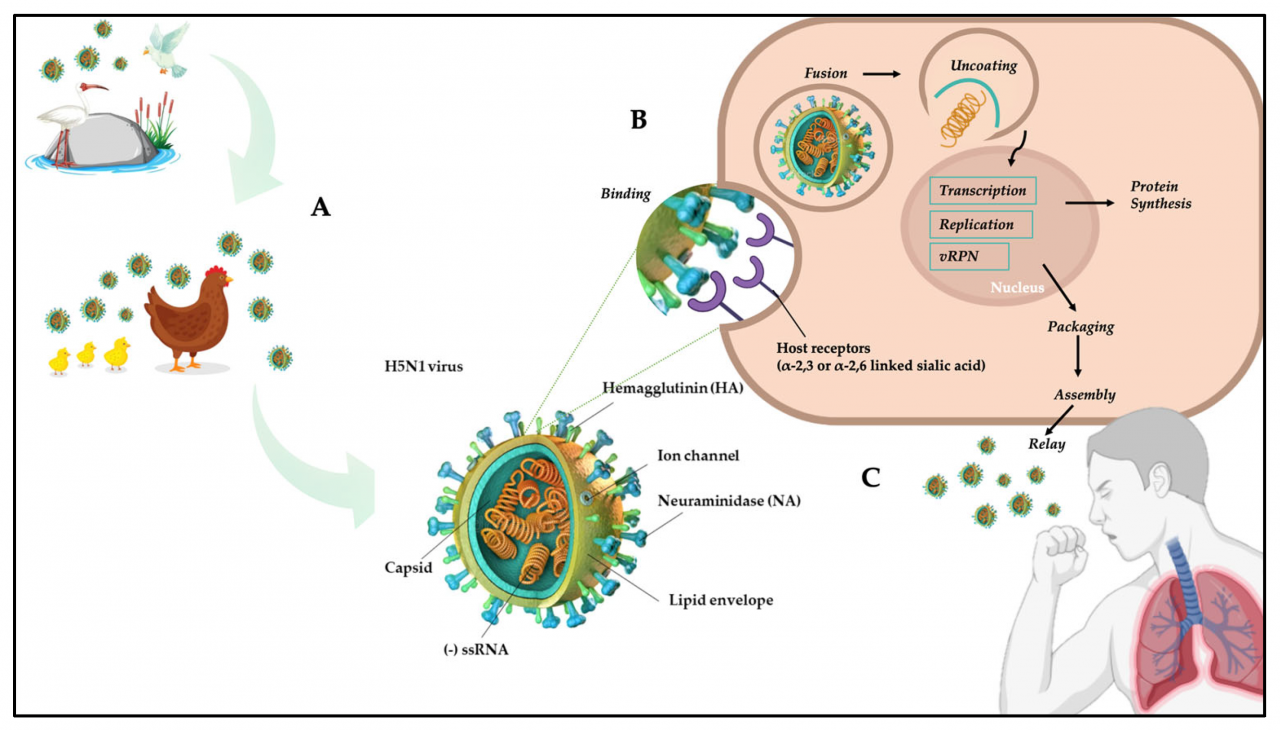
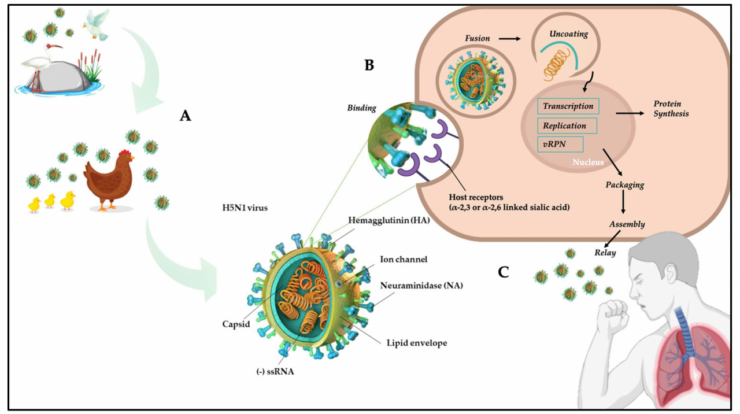
Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects birds. The H5N1 strain of avian influenza virus is one of the most virulent and deadly strains, causing significant concern due to its potential to infect and cause severe illness in humans.
History and Origins
The H5N1 virus was first identified in 1996 in Hong Kong, where it caused an outbreak in poultry and led to the death of six people. Since then, the virus has spread to over 70 countries worldwide, causing numerous outbreaks in poultry and occasional infections in humans.
Transmission and Spread
The H5N1 virus is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids. Poultry, especially chickens and ducks, are the primary reservoirs of the virus. Humans can become infected through contact with infected birds or their contaminated environments, such as farms or live bird markets.
Impact on Poultry and Livestock
Effects on Poultry and Livestock Populations
H5N1 outbreaks can have devastating effects on poultry and livestock populations. The virus causes severe respiratory illness and high mortality rates in birds, leading to significant economic losses for the poultry industry.
Economic Consequences
Outbreaks of H5N1 can result in the culling of millions of birds to control the spread of the virus. This can lead to disruptions in the poultry supply chain, price increases, and job losses in the industry.
Control and Prevention Measures
Various measures are implemented to control and prevent the spread of H5N1 in poultry and livestock. These include vaccination programs, biosecurity measures on farms, and surveillance systems to detect and respond to outbreaks.
Human Health Implications
Symptoms and Severity
H5N1 infection in humans can range from mild to severe, depending on the strain of the virus and the individual’s immune response. Symptoms may include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and respiratory distress.
Risk Factors, H5n1 who
People at higher risk of H5N1 infection include those who work with poultry or live bird markets, travelers to areas with known outbreaks, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Treatment and Prevention
There are antiviral medications available to treat H5N1 infection in humans. Preventive measures include avoiding contact with infected birds or their environments, practicing good hygiene, and getting vaccinated if recommended.
Closure

H5N1 remains a complex and evolving virus, requiring ongoing surveillance, research, and international collaboration. By understanding the nature and impact of H5N1, we can better prepare for and mitigate its potential risks, ensuring the health and well-being of both humans and animals.